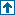



signal = pseudovoigt2d(p, x, y, {signal}) : 2D Pseudo Voigt function
iFunc/pseudovoigt2d 2D Pseudo Voigt function (fit 2D function/model)
x0=p(2); y0=p(3); sx=p(4); sy=p(5); theta=p(6) [given in deg]
a = cos(theta)^2/2/sx/sx + sin(theta)^2/2/sy/sy;
b =-sin(2*theta)/4/sx/sx + sin(2*theta)/4/sy/sy;
c = sin(theta)^2/2/sx/sx + cos(theta)^2/2/sy/sy;
signal = (a*(x-x0).^2+2*b*(x-x0).*(y-y0)+c*(y-y0).^2);
signal = p(1) * (p(8) * (1./(1+signal)) + (1-p(8)) * exp(-0.5 * 2.355* signal)) + p(7);
pseudovoigt2d([w1 w2]) creates a model with specified widths
pseudovoigt2d([ parameters ]) creates a model with specified model parameters
Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voigt_profile
P. Thompson, D.E. Cox, J.B. Hastings, J. Appl. Cryst. 1987, 20, 79.
input: p: pseudovoigt2d model parameters (double)
p = [ 'Amplitude' 'Centre_X' 'Center_Y' 'HalfWidth_X'
'HalfWidth_Y' 'Angle' 'Background'
'LorentzianRatio' ]
the rotation angle is given in degrees.
or 'guess'
x: axis along rows (double)
y: axis along columns (double)
signal: when values are given, a guess of the parameters is performed (double)
output: signal: model value
ex: signal=pseudovoigt2d([1 2 .5 .2 .3 30 .2], -2:.1:2, -3:.1:3); or plot(pseudovoigt2d);
Version: Nov. 26, 2018
See also iData, iFunc/fits, iFunc/plot, lorz
(c) E.Farhi, ILL. License: EUPL.